
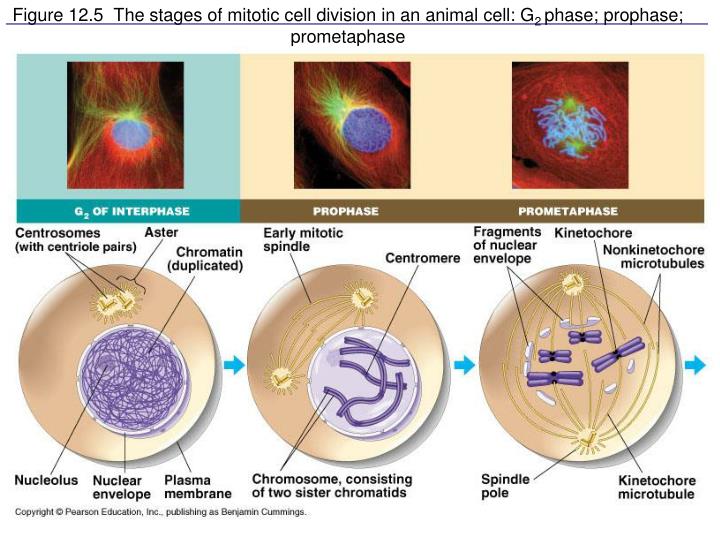
prophase, in which chromosomes are condensed, homologous chromosomes are paired together, and the spindle apparatus made of microtubules forms.Mitosis itself is composed of four phases: During M phase, the DNA chromosomes condense and are divided into the two daughter cells.G1, S, andG2 phases together are referred to as interphase. In G2 phase, the cell coordinates both transcription and translation to synthesize proteins that are required specifically for asexual cell division, or mitosis. In S phase, the DNA synthetic phase, the cell concentrates its efforts on accurately replicating its genetic material, the DNA genome. During G1 phase, the cell also transcribes and translates the genes required for DNA synthesis. G1 phase occurs after the previous cell division and is the phase where the cell grows, metabolizes, and prepares to undergo another round of cell division. G1 and G2 phases were named as gap phases, because itwas presumed that the cell did not appear to accomplish any specific events during these phases. Originally, four stages were identified: G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase. The general arrangement of the cell cycle was first determined through microscopic observations of living cells undergoing cell division. The cyclical repetition of these steps comprises the eukaryotic cell division cycle or, more simply, the cell cycle. Finally, the cellmust be able to distribute appropriately the cellular contents, including the genetic material, to the daughter cells. Next, a cell must replicate all required macromolecules, including the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), as well as the organelles. The cell achieves this status by making needed molecules, using synthetic biochemical reactions, and monitoring the outside environment to ensure continued favorable conditions for reproduction. In order for eukaryotic cell division to occur, cells must accomplish several steps.įirst, a cell must reach a sufficient size to ensure that the daughter cells will be large enough to survive. Plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they contain a nucleus and membrane-bound cellular compartments called organelles, such as chloroplasts, the sites of photosynthesis, and the central vacuole used for storage. In multicellular organisms, such as plants, cells must divide many times to produce new individuals, and additional processes of differentiation into mature cell types must occur. In unicellular species, such as bacteria and green algae, this division results in the production of new organisms. At the cellular level, growth is accomplished by a gain of mass, followed by division into two daughter cells. One of the fundamental characteristics of living organisms is their ability to grow and reproduce. In plants, as in all eukaryotic life-forms, the cell cycle comprises the processes of cell division, constituted by three preparatory phases (G, G, and S), followed by mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasm division).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
